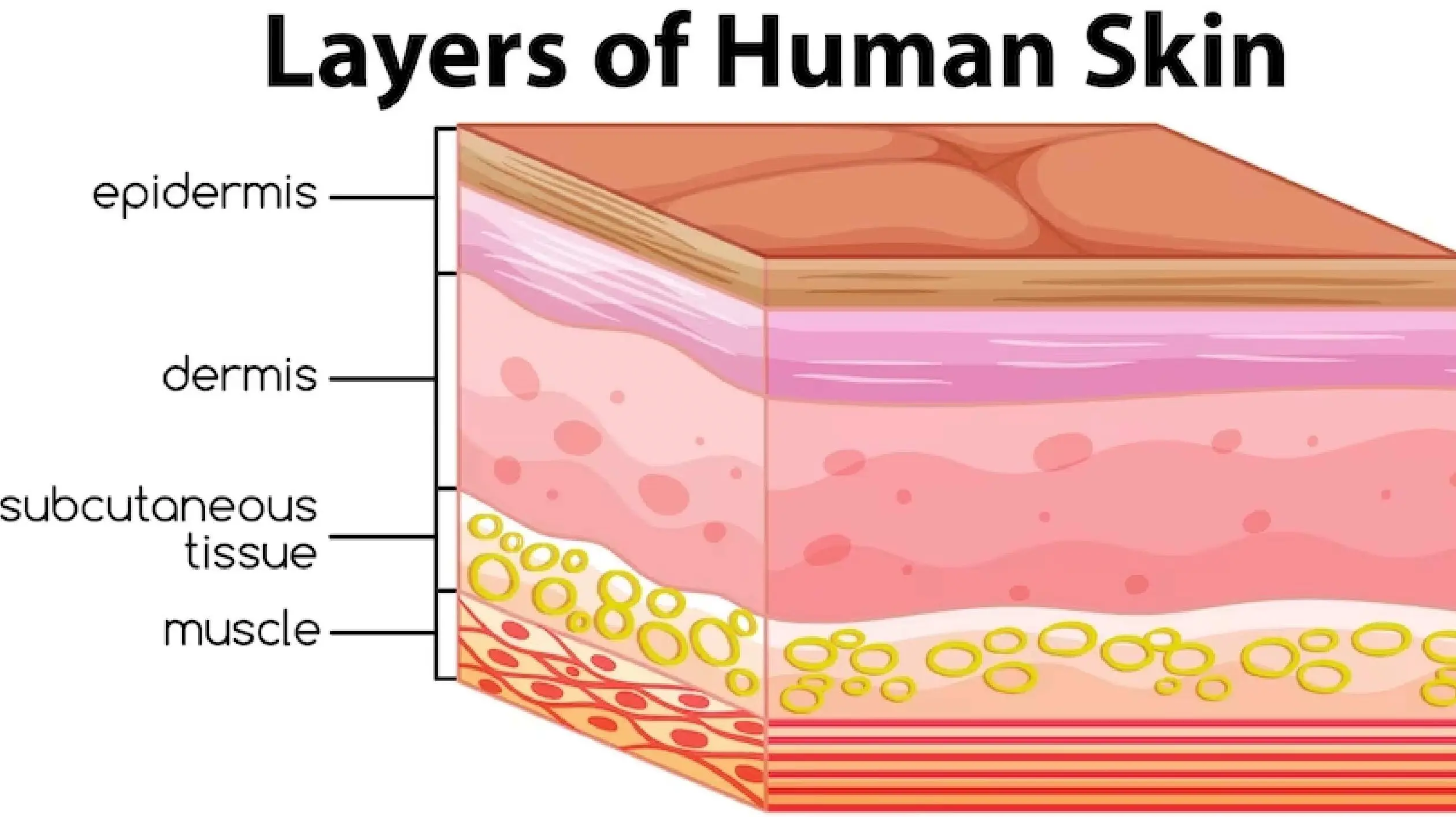
The skin is the largest organ of the human body and it is composed of seven layers. Each layer has its own distinct function and plays a vital role in protecting the body from external damage. This article will discuss the seven layers of skin and their functions, from the outermost layer to the innermost layer. It will also discuss the various treatments and conditions associated with each layer.
- The epidermis is the name of the top layer of skin. The outermost layer that is truly visible is this one. Dead skin cells that are continually being shed and replaced by new cells make up its structure. The epidermis aids in shielding us from the elements, such as rain, wind, and sunlight. It also provides us with feeling and aids in controlling body temperature.
- The dermis is the name of the skin’s second layer. The collagen and elastin fibers that make up this layer, which is thicker than the epidermis, are. The skin’s flexibility and strength come from these fibers. Additionally, the dermis houses hair follicles, sweat glands, and oil glands that keep the skin moisturized.
- The third layer of skin is the hypodermis. This layer is made up of fat and connective tissue, which helps to cushion the body and provide insulation. It also contains blood vessels and nerves, which help to regulate body temperature and provide sensation.
- The fourth layer of skin is the subcutaneous layer. This layer is made up of fatty tissue, which helps to protect the body from injury. It also helps to insulate the body and keep it warm.
- The reticular dermis is the skin’s fifth layer. Collagen and elastin fibers make up this layer, which aids in giving the skin structure. It also aids in maintaining the skin’s hydration and nourishment.
- The sixth layer of skin is the papillary dermis. This layer is made up of capillaries and small blood vessels. These vessels help to provide nutrients to the other layers of skin.
- The seventh layer of skin is the basement membrane. This layer helps anchor the other skin layers to the underlying tissue. It also helps to protect the body from infection and injury.
Which Layer of Skin Is Least Protected by Melanin
- The basal layer of skin, also known as the basal cell layer, is the deepest layer of the epidermis and the least protected by melanin. The basal layer is composed of cells that are constantly dividing to create new cells that rise up to replace dead cells shed from the surface. As these cells rise to the surface, they produce melanin, the pigment responsible for skin coloration.
- The basal layer has the fewest melanocytes, the cells that produce melanin, meaning it is the least protected from sun exposure. This layer of skin is also the least protected from external environmental factors, such as extreme temperatures, harsh chemicals, and bacteria.
Thickest Layer of Epidermis
- The thickest layer of the epidermis is known as the stratum corneum. It is the outermost layer of the epidermis and is composed of dead, flattened cells filled with keratin, a protein that gives the skin its strength and flexibility. The cells of the stratum corneum form a protective barrier against external environmental damage, such as UV radiation, and are constantly being replaced by new cells from the underlying layers.
- The stratum corneum is the layer of skin most visible to the naked eye, and it is responsible for many of the skin’s protective functions. It resists water loss and helps to maintain the skin’s moisture balance. It also helps protect against bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens. It also helps regulate body temperature by providing insulation against heat loss.
- The stratum corneum is made up of four layers of cells: the cornified layer, the granular layer, the spinous layer, and the basal layer. The cells in the topmost layer, the cornified layer, are the most deadly and flattened, and they contain the highest levels of keratin. The cells in the underlying layers are more alive and contain less keratin.
- The stratum corneum plays an important role in skin health, and its thickness and composition can vary depending on factors such as age, gender, and ethnicity. It can also be affected by environmental factors, such as exposure to sunlight, wind, and pollutants. A healthy stratum corneum is essential for maintaining the skin’s protective functions and overall appearance.
Conclusion
Each layer of skin plays an important role in keeping us healthy and protected. From the epidermis to the basement membrane, these layers work together to keep us safe from the outside world and provide the sensation and nourishment needed to stay healthy.
- The epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis are the three primary layers of the skin. The epidermis is the top layer of skin and is made up of keratinocyte-type cells. It serves as a shield to shield the body from the environment and keeps moisture in. Collagen and elastin fibers, which give the skin its strength and flexibility, are found in the dermis.
- The main layer of the skin. The deepest layer of the skin, known as the hypodermis, is made up of fat cells that act as insulation and padding. Sebaceous glands, sweat glands, and hair follicles are all found in the skin. Its primary roles are to defend the body from the elements, control body temperature, and serve as a sensory organ.
Skin is the largest organ in the human body and plays an important role in protecting our bodies from the environment. It acts as a barrier to bacteria, viruses, and other environmental contaminants, helping to keep us healthy. It also helps to regulate body temperature and fluid balance, and it produces vitamin D when exposed to sunlight. Additionally, skin provides an important sense of touch, which helps us to interact with the environment.
There are five varieties of skin: normal, dry, oily, combination, and sensitive.
The skin is an organ. It is the largest organ of the human body, and it plays an important role in protecting the body from pathogens, regulating body temperature, and synthesizing vitamin D.
Skin is an organ because it is a complex structure that performs multiple functions for the body. It is the largest organ in the body and acts as a protective barrier from environmental harm and foreign invaders. Skin also helps regulate body temperature, provides protection against dehydration, and plays a role in the production of Vitamin D.